
Guest Post by Jonathan Roberts
Let’s get one thing out of the way right now.
A map shouldn’t be pretty.
I know what you’re thinking – those posters of Middle Earth are gorgeous. Of course a map should be beautiful! But for worldbuilding purposes a pretty map is a Very Bad Thing. Beautiful things are precious, and we tend to want to leave precious things pristine and untouched. When we’re building worlds we need to break things, and often. So, out with any thoughts that we’re making a pretty map. We’ll be making a functional map. In fact we’ll be making many maps, one after the other. In exactly the same way that your notes are not the final manuscript, a map isn’t the final world. It’s a visual notepad, and you should be crossing things out, erasing sections and rebuilding from scratch as you go along.
So we won’t be needing photoshop today, we need a pad of scratch paper and a pencil. Ready? Right, let’s build a world.
First of all, think about the world you need to build. In many cases this is a defined area that’s much smaller than the planet you’re on. Very few stories truly span a globe, so let’s begin by cutting down to the area that the story explores. This keeps the work focused on a reasonable area, and means there will always be distant and mysterious lands to explore down the line.
In your tale there will be nations, city states or power centers of some form. Start by making a note of their relationships to one another. Are they at war? Are they aloof? Do they feud over resources or are they closely allied? Think over the things that make them stand out. Are they famous for their expansive grain fields? Their iron? Their navy? I’m sure you can see the theme here. Nations are defined by the geography they inhabit as much as we define the geography by the nation. A nation with a large navy needs sea access, but it should also have natural defenses like a mountain range that allows the nation to neglect other military forces in favor of its navy. Two countries at war need to be close, and need to have a means of attacking one another.
Focus on major terrain at this point–how much coastline and mountain range. Make notes about other terrain that comes to mind–the tulip fields of Alak’tor, the salt mines of Keshel. Those will come in useful later.
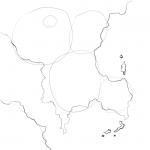
It’s now time to start our map. Grab a pencil and faintly draw in circles where your nations are. Nations that are allies or at war should be close. Those that rarely interact should be farther away, or have an insurmountable natural barrier between them. Drawing circles on a map may sound easy, but this stage can take a few tries to get the relationships right.

But circles aren’t really a map. Let’s draw some coastlines. Think about which of your nations need large coastlines and which should be landlocked. Then let your pen wander. Really – avoid straight lines. Coastlines are jagged and broken things. If your line doesn’t look like it was plotted by a drunken ant, you’re doing it wrong.
Now let’s lay in some mountains. Mountains tend to form ridges. Avoid the temptation to fill in whole blocks of land with mountains. Instead, lay them out in wavy lines. They often follow the edge of a coastline (think the Andes). From a story point of view, they form obstacles for your heroes and they create natural boundaries between nations, or between nations and the great unknown. Mountains also create boundaries between climates. So if you need a desert in one area and a jungle in the other, you’d better place a mountain range between them to stop the rain from the jungle getting to the desert.
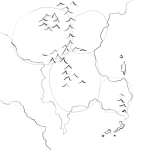
Next up, we have rivers. Rain falls on mountains and runs downhill to the sea. It always flows to the lowest point – and there’s always one lowest point. This means that rivers don’t branch as they flow to the sea, they only join. So – no rivers going from coast to coast. At some point that requires water to flow uphill. No lakes that have two separate rivers leading to the sea – remember, only one lowest point leading out. Think of a river like a tree. There’s one trunk where it enters the sea, but a panoply of branches reaching towards the mountains.
Rivers are also strategically important. There’s hardly a river mouth in the world without a town on it and most great cities lie on a river. If you know where your cities are going to be, make sure there’s a decent sized river flowing through them. Equally, rivers make great defenses. It’s hard to build a wall all the way along your nation’s border, but it’s almost as hard to get an army over a well-defended river as it is to have them scale a wall.
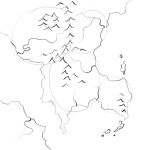
Add some hills to the edge of your mountain ranges. Lay in some forest and see how it looks. Remember, don’t be precious. If you don’t like it, start on a new sheet of paper. Sketch another coastline. Turn it upside down.
When you’re happy with the terrain, go over the pencil lines with pen, and erase the pencil–including your nation boundaries. Scan and photocopy the map. Go away and have some food.
When you come back, try the following experiment. Ignore your previous nations. Look at the virgin world with a new eye. If you were founding a country in the world, where would you start? What would be the key strategic choke points? Look at the world as if you were playing Civ. Where are the resources you need to defend, what lands would you try to annex? Use some colored pencils to sketch in different nations and boundaries. Edit the rivers if you need to, move things around. You’ve got lots of copies of the map–experiment.
Once you have a layout you like, we’ll add cities.
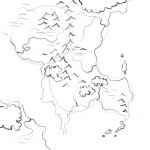
Cities are where they are for a reason. They don’t just appear up in the middle of nowhere. Population centers need food, water, trade and security. Rivers can provide all of these, which is why towns and cities tend to spring up at river mouths. Locate your capitals in places that are easily defended and that have good transport connections to the rest of the nation. Place smaller cities in key locations, whether that’s in the heart of a mining community on the edge of a mountain range, at a key strategic river crossing, or a market town in the middle of leagues of prime cattle-ranching land. At this point, also mark in major fortifications.
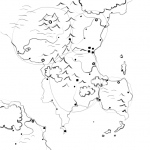
With these indicated it’s a simple matter to place the roads. These will connect the major cities, the main food producing regions, and any other major trade routes.
You now have a perfectly functional map! But remember, nothing is set in stone. Each time you run through this process your map will be better. Each time you sketch the map you’ll have new ideas. As you continue to write about your world you’ll come up with new thoughts on what terrain you should have, how two countries relate across their border, where a great wilderness needs to be. Redraw the map – it’s there for you. Both your map drawing and your text will be better for the relationship between map and story.
And when your manuscript is ready to go from draft to final, your map will be ready to go from sketch to illustration. But that’s a post for another day.
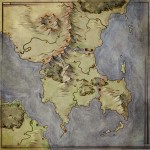
If you want to learn about the art of mapmaking, then check out the Cartographers’ Guild, or my own tutorials.


 new adult genre was on the rise, in part due to the college age of the main character. My characters haven’t quite fit anywhere other than new adult, and I wanted a smaller publisher willing to go to bat for me and my characters without trying to force them into a different genre (like every other agent and editor I sent it to). TWCS had first-hand experience of launching a mega-hit and I wanted to take advantage of all that in marketing my book, Lightning Rider.
new adult genre was on the rise, in part due to the college age of the main character. My characters haven’t quite fit anywhere other than new adult, and I wanted a smaller publisher willing to go to bat for me and my characters without trying to force them into a different genre (like every other agent and editor I sent it to). TWCS had first-hand experience of launching a mega-hit and I wanted to take advantage of all that in marketing my book, Lightning Rider.
